Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points Certification Process in Nepal
HACCP (Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points) Certification is a vital food safety management system that helps organizations in Nepal maintain the highest standards of food safety. Quality Management System in Nepal Pvt. Ltd. is a trusted certification body, providing expert guidance to businesses seeking HACCP Certification. In this comprehensive article, we will delve into the fundamental aspects of HACCP, its principles, benefits, implementation, and how Quality Management system Nepal Pvt.Ltd.plays a crucial role in achieving HACCP Certification.
HACCP Full Form and Meaning
HACCP stands for "Hazard Analysis and Critical Control
Points." It is a systematic approach to food safety that identifies and
manages potential hazards, ensuring safe food production and distribution.
What are the History of HACCP?
The history of HACCP dates to the 1950s when it was
developed as a food safety system by a team of researchers at the Pillsbury
Company in collaboration with NASA (National Aeronautics and Space
Administration) and the U.S. Army Laboratories. The primary objective was to
ensure the safety of food for astronauts during space missions.
Here is a brief overview of the key milestones in the history of HACCP:
- 1950s
- Development of HACCP Concept: The concept of HACCP was first introduced
by Dr. Howard Bauman, a food microbiologist at Pillsbury, along with a
team of scientists. They developed a systematic approach to identify and
control potential hazards in food production.
- 1960s
- Adoption by NASA: In the early 1960s, NASA adopted the HACCP system for
its space programs to ensure the safety of food consumed by astronauts
during space missions. The critical control points and monitoring
procedures were essential to guarantee the safety and quality of space
food.
- 1970s
- Application in Food Industry: The HACCP system gradually gained
recognition in the food industry. Organizations and regulatory authorities
started recognizing its significance in ensuring food safety. The United
States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the World Health
Organization (WHO) acknowledged HACCP as an effective preventive approach.
- 1980s
- Codex Alimentarius: In 1985, the Codex Alimentarius Commission
(CAC), a joint body of the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) and the
World Health Organization (WHO), published the first Codex HACCP
Principles. These principles provided guidelines for the application of
HACCP in international food trade.
- 1990s
- Widespread Implementation: Throughout the 1990s, HACCP gained
significant momentum worldwide. Many countries and international food
organizations adopted HACCP as a standard for food safety. The HACCP
system became a fundamental requirement for food businesses.
- 2000s
- Integration with ISO Standards: HACCP was integrated into
international standards. The ISO 22000 standard, published in 2005,
combined HACCP principles with other management system requirements,
allowing organizations to implement a comprehensive food safety management
system.
- Present
- Continued Advancements: HACCP continues to evolve and adapt to
changes in the food industry. It remains a critical tool for ensuring food
safety and preventing foodborne illnesses. The principles of HACCP are
widely applied by food businesses globally to meet regulatory requirements
and maintain consumer trust.
Today, HACCP is considered a cornerstone of food safety
management systems, providing a systematic and science-based approach to
identify, evaluate, and control food safety hazards throughout the food supply
chain. Its history and development demonstrate its effectiveness in
safeguarding public health and ensuring the delivery of safe and high-quality
food products.
HACCP Guidelines
HACCP is a systematic and preventive approach to food safety that helps identify, evaluate, and control potential hazards throughout the food production and handling process. HACCP guidelines are a set of principles and procedures that food businesses follow to ensure the safety of their products and prevent foodborne illnesses. The guidelines are widely recognized and implemented in the food industry worldwide.
7 Principles of HACCP
The seven basic principles of HACCP, as defined by the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA), are as follows:
- Conduct
a Hazard Analysis: Identify potential hazards associated with the
production and handling of the food product. These hazards can be
biological, chemical, or physical.
- Determine
Critical Control Points (CCPs): Critical Control Points are the stages in
the food production process where hazards can be prevented, eliminated, or
reduced to acceptable levels. These points are crucial for maintaining
food safety.
- Establish
Critical Limits: Critical Limits are the maximum and minimum values set
for each Critical Control Point. They define the acceptable limits to
which a process should be controlled to prevent or eliminate hazards.
- Establish
Monitoring Procedures: Monitoring involves regularly observing and
recording data at Critical Control Points to ensure that the process
remains within the established critical limits.
- Implement
Corrective Actions: When monitoring indicates that a Critical Control
Point is not within the established critical limits, corrective actions
are taken to bring the process back under control and prevent unsafe
products from reaching consumers.
- Establish
Verification Procedures: Verification involves periodic review and
evaluation of the entire HACCP system to ensure it is working effectively
in controlling hazards.
- Establish
Record-Keeping and Documentation Procedures: Accurate records and
documentation are crucial for the successful implementation of HACCP.
Records provide evidence that the system is functioning correctly and can
be useful for audits and inspections.
It is important to note that HACCP guidelines are not only limited to food production but can also be applied to various other industries such as pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and more, to ensure safety and prevent potential hazards at critical points in the manufacturing process.
Advantages of HACCP
The advantages of HACCP include reduced foodborne illnesses, enhanced consumer confidence, and compliance with food safety regulations which are given below in more details:
- Enhanced
Food Safety: The primary advantage of HACCP is its ability to
significantly improve food safety. By systematically identifying and
controlling hazards at critical points in the food production process, the
risk of foodborne illnesses and contamination is greatly reduced.
- Prevention
rather than Inspection: Unlike traditional inspection-based
systems, HACCP focuses on prevention rather than detection. By proactively
monitoring and controlling critical points, potential hazards can be
addressed before they become a problem, leading to safer food products.
- International
Recognition: HACCP is recognized and accepted globally as a
reliable and effective food safety management system. Its widespread use
has created a standard framework for ensuring food safety across borders
and industries.
- Cost-Effective: Implementing
HACCP can lead to cost savings in the long run. By preventing food safety
issues, businesses can avoid costly recalls, legal actions, and damage to
their reputation.
- Increased
Consumer Confidence: Consumers are becoming more conscious of
food safety, and the presence of a HACCP-based system can instill
confidence in the products they purchase. This can lead to improved
customer loyalty and increased market competitiveness.
- Better
Quality Control: HACCP requires a systematic approach to
monitoring and documentation, leading to better overall quality control in
the food production process. Consistent quality can enhance the reputation
of the brand or business.
- Legal
and Regulatory Compliance: Many countries have made HACCP a
mandatory requirement for certain food businesses. By implementing HACCP,
companies can ensure they are in compliance with food safety regulations,
avoiding potential legal issues and penalties.
- Continuous
Improvement: HACCP encourages a culture of continuous
improvement. Regular review and verification of the system allow for
adjustments and updates to keep up with changing hazards, technology, and
best practices.
Benefits of Implementing HACCP
Implementing HACCP benefits organizations by improving food
safety, reducing product recalls, and protecting brand reputation which are as follows:
- Risk
Reduction: Implementing HACCP helps reduce the risk of foodborne
illnesses and product recalls, protecting both consumers and the reputation
of the business.
- Increased
Efficiency: HACCP streamlines processes by focusing on critical
control points, leading to more efficient operations and reduced wastage.
- Employee
Training: HACCP requires well-trained staff to implement and maintain
the system effectively. This investment in employee training can lead to a
more skilled and knowledgeable workforce.
- Traceability:
HACCP emphasizes accurate record-keeping, ensuring that the origin and
journey of raw materials and products can be easily traced in the event of
a safety concern.
- Competitive
Advantage: Companies with a certified HACCP system may gain a
competitive advantage over those without one. Many buyers and retailers
prioritize suppliers with robust food safety management systems.
- Global
Market Access: For businesses looking to export their products, HACCP
certification may be a prerequisite for accessing international markets
with stringent food safety regulations.
- Supplier
and Customer Confidence: HACCP instills confidence not only in
customers but also in suppliers who are assured that their products are
being used in a safe and responsible manner.
- Crisis
Management: Having a HACCP plan in place can improve a company's
ability to handle crises related to food safety effectively.
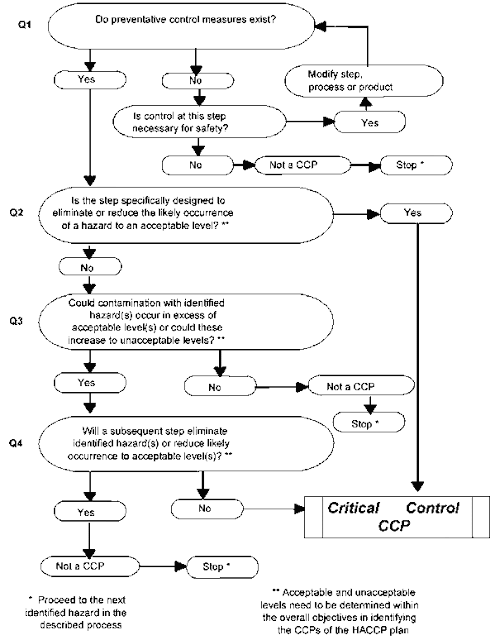
HACCP Critical Control Points
Critical Control Points (CCPs) are essential stages in the
food production process where specific actions are taken to prevent, eliminate,
or reduce identified hazards to an acceptable level. These points are crucial
for ensuring food safety. Some examples of HACCP Critical Control Points
include:
- Cooking
Temperature: Ensuring that food is cooked to the appropriate internal
temperature to eliminate harmful pathogens and bacteria.
- Cooling
and Refrigeration: Monitoring and controlling the cooling and
refrigeration processes to prevent bacterial growth in perishable foods.
- Storage
Conditions: Maintaining proper temperature and humidity levels during
storage to prevent spoilage and contamination.
- Cross-Contamination
Prevention: Implementing measures to prevent cross-contamination
between raw and cooked foods during processing.
- Chemical
Usage: Controlling the proper use and storage of chemicals to avoid
accidental contamination.
- Product
Labeling and Allergens: Ensuring accurate labeling to prevent allergen
cross-contact and allergic reactions in consumers.
- Packaging
Integrity: Verifying that the packaging is intact and secure to
prevent physical contamination.
- Cleaning
and Sanitation: Implementing effective cleaning and sanitation
procedures to prevent microbial contamination.
- Supplier
Verification: Ensuring that raw materials from suppliers meet the
necessary safety standards.
- Shipping
and Distribution: Monitoring temperature and handling during shipping
and distribution to preserve product quality and safety.
HACCP Corrective Action Examples
Corrective actions in HACCP are taken when monitoring at
Critical Control Points indicates a deviation from established critical limits.
Examples of HACCP corrective actions include:
- Adjusting
Cooking Temperatures: If the cooking temperature falls below the
critical limit, the food may be cooked for a longer time or at a higher
temperature to ensure safety.
- Enhancing
Sanitation Practices: If sanitation practices are not sufficient,
increased cleaning frequency or more rigorous cleaning procedures may be
implemented.
- Employee
Training: If deviations are attributed to human error or lack of
knowledge, additional training and education may be provided to the
employees involved.
- Isolating
Contaminated Products: If a contamination event is detected, affected
products may be isolated and removed from the production line to prevent
further distribution.
- Investigating
Root Causes: Conducting thorough investigations to identify the root
cause of the deviation and implementing measures to prevent its recurrence.
- Revising
Critical Limits: If critical limits are consistently being exceeded,
they may be revised based on new data or scientific evidence.
- Notifying
Management: Communicating deviations and corrective actions taken to
the management team for appropriate decision-making.
HACCP Elements
The HACCP system consists of several essential elements that work together to ensure food safety. These elements are:
- Conducting Hazard Analysis: Identifying and assessing potential hazards associated with the food production process
- Establishing
Critical Limits: Setting specific criteria for each Critical Control
Point to maintain food safety.
- Monitoring:
Regularly checking and recording data at Critical Control Points to ensure
they remain within the established critical limits.
- Verification:
Periodically reviewing and evaluating the entire HACCP system to confirm
its effectiveness.
- Record-Keeping:
Maintaining detailed records of hazard analysis, critical limits,
monitoring results, and corrective actions taken.
Four HACCP Principles
- Conduct
Hazard Analysis: Identify potential hazards at each stage of food
production, processing, and distribution.
- Determine
Critical Control Points (CCPs): Identify points in the process where
hazards can be controlled or eliminated.
- Establish
Critical Limits: Set specific criteria for each CCP to ensure food
safety.
- Implement
Monitoring Procedures: Establish measures to monitor CCPs and take
corrective action when necessary.
When Should Your HACCP Plan Be Refreshed?
HACCP plans should be reviewed and refreshed regularly,
especially when:
- There
are changes in the food production process, equipment, or ingredients.
- New
food safety regulations or guidelines are introduced.
- Incidents
of foodborne illnesses occur, necessitating a reevaluation of the plan's
effectiveness.
What Are the Features of HACCP?
HACCP offers several key features that make it a robust food
safety management system:
- Preventive
Approach: HACCP focuses on preventing hazards rather than detecting them
after the fact.
- Customizability:
HACCP plans can be tailored to specific food production processes, making
them adaptable to various industries.
- Scientific
Basis: HACCP decisions are based on scientific evidence, ensuring the most
effective risk management.
- Continuous
Improvement: Regular review and improvement of the HACCP plan ensure
ongoing food safety enhancement.
Where to Obtain Certifications in HACCP?
Quality Management System Nepal Pvt. Ltd. is a reputable provider
of HACCP certification services in Nepal. With experienced professionals and a
customer-centric approach, they guide organizations in achieving HACCP
certification, instilling trust in consumers and regulatory authorities.
How to Get HACCP Consultants?
Finding reliable HACCP consultants is essential for a
successful certification journey. Quality Management System Nepal Pvt. Ltd. offers
expert HACCP consulting services, providing comprehensive guidance in
developing, implementing, and maintaining HACCP plans. Their consultants assist
in conducting hazard analysis, establishing CCPs, defining critical limits, and
ensuring compliance with HACCP principles.
Conclusion:
HACCP Certification in Nepal is an indispensable asset for businesses in the food industry. With the support of Quality Management System in Nepal Pvt. Ltd., organizations can implement a robust food safety management system, prevent foodborne hazards, and gain a competitive edge. By adhering to the four HACCP principles, regularly refreshing the HACCP plan, and seeking assistance from reputable HACCP consultants, businesses can ensure food safety and build a strong reputation in the market.
Frequently Asked Questions:
What is HACCP Certification in Nepal?
What is HACCP?
What Does HACCP Stand For?
What is Meant by HACCP?
HACCP means implementing a food safety management system that identifies and manages hazards at critical points to ensure safe food production and distribution.
How to Get HACCP Certification?
To obtain HACCP Certification, businesses must develop and implement a HACCP plan, undergo an internal audit, and pass a certification audit conducted byQuality Management System in Nepal Pvt. Ltd
What is HACCP
Certification?
HACCP (Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points) Certification is a food safety management system that ensures the safe production and handling of food products.
Why is HACCP
Certification important?
HACCP Certification is crucial to identify and control potential hazards in food production, ensuring consumer safety and compliance with food safety regulations.
How to get HACCP
Certified in Nepal?
To obtain HACCP Certification in Nepal, businesses need to implement a HACCP plan and undergo a certification audit by an accredited certification body like Quality Management System Nepal Pvt. Ltd.
What are the benefits
of HACCP Certification?
HACCP Certification enhances the credibility of food businesses, improves food safety practices, reduces the risk of foodborne illnesses, and increases marketability in the food industry.
Is HACCP Certification
mandatory in Nepal?
While HACCP Certification is not mandatory in Nepal, many food businesses opt for it voluntarily to demonstrate their commitment to food safety and gain a competitive edge.
What is the process of
HACCP Certification?
The process involves identifying potential hazards, establishing critical control points, implementing control measures, and conducting regular audits to ensure compliance.
Can small food
businesses get HACCP Certified?
Yes, HACCP Certification is applicable to businesses of all sizes. Quality Management System Nepal Pvt. Ltd. provides guidance tailored to small food businesses' needs.
What industries can
benefit from HACCP Certification?
HACCP Certification benefits industries involved in food production, processing, packaging, distribution, and storage, including restaurants, hotels, and catering services.
How long does it take
to get HACCP Certified?
The time required for HACCP Certification depends on the organization's readiness and the complexity of its food safety management system. It typically takes a few months.
Is HACCP a zero risk?
Does ISO 22000 cover HACCP?
Which ISO certification is best for the food industry?
What is the highest HACCP level?
Who is the head of HACCP?
Is HACCP a qualification?
What is the duration of HACCP certification?
Which is better, HACCP, or ISO 22000?
Is HACCP a QMS (Quality Management System)?
What is HACCP Certification, and why is it important?
HACCP (Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points)
Certification is a systematic approach to identify, evaluate, and control
hazards related to food safety. It ensures that food products are safe for
consumption and free from potential health risks. HACCP Certification is vital
for businesses involved in food production, processing, and distribution to
demonstrate their commitment to food safety and comply with international
standards.
How does HACCP Certification benefit my business?
HACCP Certification
can bring several advantages to your business. It enhances your credibility and
reputation in the market, giving customers confidence in the safety of your
food products. It also improves your compliance with legal and regulatory
requirements, which can open up new business opportunities and partnerships.
Additionally, HACCP Certification helps in reducing food-related risks and
minimizing the chances of foodborne illnesses, ensuring customer satisfaction
and loyalty.
What are the key steps in obtaining HACCP Certification?
The process of obtaining HACCP Certification involves
several key steps. These include conducting a hazard analysis to identify
potential food safety hazards, determining critical control points (CCPs),
setting critical limits for each CCP, establishing monitoring procedures,
implementing corrective actions, and maintaining thorough documentation. Once
your HACCP plan is in place and meets the standards, you can approach a
certification body for evaluation and certification.
How long does it take to get HACCP Certification?
Answer: The duration to obtain HACCP Certification depends
on various factors, including the complexity of your food production process
and the efficiency of implementing the HACCP plan. Generally, the certification
process can take several weeks to a few months, from the initial assessment to
the final certification decision. However, the timeline may vary based on the
certification body and the readiness of your organization.
Is HACCP Certification mandatory for food-related businesses in Nepal?
While HACCP Certification is not a legal requirement in Nepal, it is highly recommended and considered an industry best practice for businesses involved in food processing, manufacturing, and distribution. Having HACCP Certification demonstrates your commitment to food safety and quality, making it easier to comply with food safety regulations and meet customer expectations.
Can Quality Management System in Nepal Pvt. Ltd. assist us in obtaining HACCP Certification?
Absolutely! Quality Management System Nepal Pvt. Ltd. is a leading certification body with expertise in various ISO standards, including HACCP. We have a team of experienced auditors who can guide you through the entire certification process, from developing your HACCP plan to conducting the final audit. Our aim is to help your business achieve HACCP Certification efficiently and smoothly.
How long is the validity of HACCP Certification?
The validity of HACCP Certification typically ranges from one to three years, depending on the certification body's policies. During this period, regular surveillance audits may be conducted to ensure your continued compliance with HACCP principles. It is essential to maintain the HACCP system effectively and update it as needed to ensure continuous certification.
Can HACCP Certification be integrated with other ISO certifications?
Yes, HACCP Certification can be integrated with other ISO
certifications like ISO 9001 (Quality Management System) and ISO 22000 (Food
Safety Management System). Integrating multiple certifications streamlines your
management systems, reduces duplication of efforts, and enhances overall
efficiency. Quality Management System Nepal Pvt. Ltd. can provide guidance on
integrating HACCP with other ISO standards for maximum benefit.
For further inquiries or to start your journey towards HACCP Certification, feel free to contact Quality Management System Nepal Pvt. Ltd. Our expert team is ready to assist you in achieving excellence in food safety and quality management.
In order to maintain a seamless and efficient ISO
certification process, partnering with a trusted ISO consultant is crucial. At
Quality Management System Nepal Pvt. Ltd., we are committed to providing your
organization with expert guidance and support, ensuring a cost-effective and
successful ISO implementation journey. As the leading ISO System Certification
body in Nepal, we offer a comprehensive range of certification services
tailored to your organization's needs.
Explore our range of ISO certification services:
- ISO 55001 Certification in Nepal: Enhance asset
management and energy efficiency.
- TL 9000 Certification in Nepal: Elevate quality
standards in the telecommunications industry.
- IATF 16949 Certification in Nepal: Elevate automotive
quality and meet industry requirements.
- ISO 37001 Certification in Nepal: Strengthen
anti-bribery management systems.
- AS 9001 Certification in Nepal: Attain aerospace quality
standards for excellence.
- ISO FSSC 22000 Certification in Nepal: Ensure safe and
quality food production.
- ISO 29990 Certification in Nepal: Elevate training and
learning services.
- ISO SA 8000 Certification in Nepal: Prioritize social
accountability and ethical practices.
- ISO 27017 Certification in Nepal: Ensure secure cloud
computing environments.
- ISO 20000-1:2018 Certification in Nepal: Elevate IT
service management systems.
- ISO 22301 Certification in Nepal: Enhance business
continuity and resilience.
- ISO 41001 Certification in Nepal: Optimize facility
management systems.
- HACCP Certification in Nepal: Ensure food safety and
hazard analysis.
- ISO 50001 Certification in Nepal: Enhance energy
management and efficiency.
- ISO 13485 Certification in Nepal: Elevate medical device
quality standards.
- Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) Certification in Nepal:
Ensure quality and compliance in manufacturing.
- ISO 9001 Certification in Nepal: Elevate overall quality
management.
- ISO 15189:2022 Certification for Medical Laboratories in
Nepal: Elevate medical laboratory practices.
- ISO 17025 Certification for Testing and Calibration
Laboratories in Nepal: Ensure accurate testing and calibration.
- ISO 27001:2022 Certification for Information Security in
Nepal: Enhance information security practices.
- ISO 22000 Certification for Food Safety Management System in
Nepal: Ensure safe and quality food production.
- ISO 45001:2018 Certification for Occupational Health and
Safety in Nepal: Elevate health and safety standards.
- ISO 14001:2015 Certification for Environmental Management in
Nepal: Enhance environmental sustainability.
Our dedicated team is ready to provide your organization
with customized solutions and expert assistance. If you have any queries or are
ready to embark on your ISO certification journey, feel free to contact us at
9840525565 for a free consultation on our ISO certification services. Trust Quality Management System in Nepal Pvt. Ltd. to be your partner in achieving excellence and
compliance.

.png)